Network mapping:
Network mapping is the process of understanding and visualizing a network’s physical and logical connections.
Nmap is a popular network mapping tool. Nmap enables administrators to identify the devices operating on their systems, discover open ports, and detect security risks.
Wireshark is a powerful network protocol analyzer. Wireshark provides visibility into the specific network traffic details.
IT and cybersecurity professionals can leverage network mapping to manage the network’s complexity, easily troubleshoot issues, detect anomalies in the network, proactive network management and strategic planning, efficient documentation.
The attackers can leverage network mapping to identify unguarded entry points, vulnerable systems, defenses,
navigate the network, prioritize target segments, deduce high-value assets, craft tailored phishing campaigns,
or social engineering attacks.
Packet sniffling:
Packet sniffing, is a technique used to capture and analyze data packets traveling through a network. IT professionals use packet sniffing for network troubleshooting, performance monitoring, and activity oversight. Attackers use packet sniffing to steal sensitive information like login credentials, personal details, and financial data. There are two primary sniffing tactics, passive and active sniffing. The key strategies to protect network security against unauthorized packet sniffing include: system updates, strong login measures, vigilant email practices, VPN usage, and prioritizing HTTPS encrypted websites.
IP spoofing:
IP spoofing involves manipulating packet headers to alter the source address, effectively concealing the true origin of the sender or pretending to be another host.
DDoS commonly employs IP spoofing and floods a target with excess traffic, disrupting services.
A botnet refers to a collection of interconnected computers centrally controlled by one or more attackers.
The man-in-the-middle strategy is to intercept the exchange between two systems, modify the packets and then forward them undetected by the authentic communicator or recipient.
IP spoofing poses challenges to law enforcement and cybersecurity teams.
IP spoofing can be limited usingthe following techniques; ingress filtering, which establishes a critical
network security measure where traffic is inspected and managed at the point of entry to the network, egress filtering, which specific networks deploy as an added layer of protection.
What is a DoS attack?
A denial of service (DoS) attack is an attempt to overload a website or network, with the aim of degrading its performance or even making it completely inaccessible. Typically a successful DoS attack will result in loss of availability of part, or all, of a system, and consume time and money to analyse, defend and recover from. A distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack is a form of DoS attack that originates from more than one source. DDoS attacks are typically more effective than attacks from a single source because they usually generate more attacking traffic. The fact that traffic is spread across many sources also makes it harder to distinguish attacker traffic from legitimate traffic.
How to prepare for a DDOS attack. See this overview.
Injection attacks:
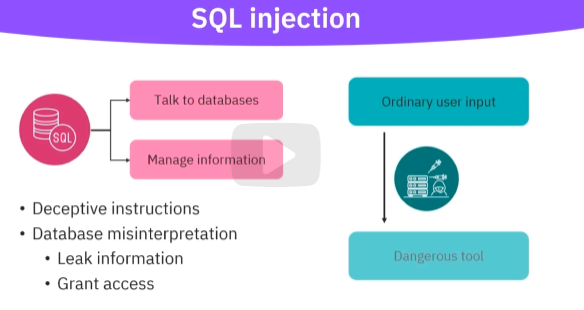
Injection attacks are cyber attacks, where an attacker injects malicious code into a query, web application, or system, triggering remote commands that manipulate website data.
There are two popular injection attacks, SQL injection and XSS.
Attackers exploit SQL injection vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access and compromise sensitive information.
The major consequences of SQL injection attacks include confidentiality breach, authentication compromise,
authorization loss, and integrity violation.
XSS attacks are security breaches where attackers embed harmful scripts into web pages. There are two types of XSS attacks, server XSS and client XSS.


